Retraining: requirements, forms, financing, tips
Content
- What is retraining?
- Forms: What types of retraining are there?
- The most common reasons for retraining
- Is it worth retraining?
- Retraining requirements
- Retraining: which professions are in demand?
- Financing retraining
- Tips for a successful retraining
Retraining is the gateway to a new career. Be it a professional reorientation for health reasons or the lateral entry and restart in another profession: Thanks to a state-funded retraining or privately paid training and further education, the career step can be successful. However, it is tied to requirements. Find out here what you need to consider when retraining, how the financing works and under what conditions you can receive funding ...
What is retraining?
Retraining is a path to professional reorientation. It is a form of professional development: The aim is not, however, to deepen or expand the existing knowledge from your own specialist area. The retraining is intended to acquire new skills and requirements for changing jobs to another professional field.
The retraining is regulated in Section 1, Paragraph 5 of the Vocational Training Act. They are intended to enable employees to react flexibly to changes in the labor market. Most retraining courses in Germany are funded and funded by pension insurance, job centers or employment agencies. This process takes up to two years - depending on the employee's professional training.
Retraining can be carried out at school or as a dual (company or inter-company). In addition, internships usually have to be completed. We present the different forms in more detail:
Forms: What types of retraining are there?
- School retraining
With this retraining measure, the advanced training takes place exclusively in a vocational school or vocational school. Internships ensure more practical relevance. - Dual retraining (operational)
As with classic training, this type of retraining has a practical and a theoretical part. The practical takes place in the training company, the theoretical in the vocational school. The big advantage: those who retrain the dual retraining receive a fixed training salary. - Inter-company retraining
Here, private educational institutions take on the practical lessons, often also the theoretical part of the vocational school. In some cases, internships are also required. It is also the most expensive form of retraining. Therefore, it is usually paid by the Federal Employment Agency or another service provider.
Part-time retraining is also possible. This part-time method cuts weekly working hours by a quarter or more. You attend the vocational school full-time. The model is primarily intended for parents who have to arrange a change of job and childcare.
The most common reasons for retraining
After five, ten or maybe even 20 years of professional experience in a job, do a retraining and start all over again? This is - admittedly - not an easy step. Contacts and the earned salary are lost, not every employer hires lateral entrants.
Retraining can provide better opportunities on the job market. There are several reasons for such a radical job change at the age of 30, 40 or 50. The most common include:
- Job frustration
Some people realize that they will not be happy at all in the profession they have learned. If you don't want to torment yourself for eight hours every day for the next few years or even decades, you can look for retraining and a new start. - unemployment
Not every job is sought in the same way on the job market. In the event of impending or existing unemployment, retraining can be the necessary step to reposition yourself. - illness
Whether it's an accident at work, an illness or other health reasons: Retraining due to illness is one of the most common reasons. If you can no longer do your job, you will have to reorient yourself. - absence
After a long absence from work, the way back is not always easy. This can be due to a long illness, but also parental leave of up to three years. If the re-entry does not work (or is not wanted), the retraining can open new doors.
These personal reasons are irrelevant for the retraining itself. At best, they are a factor when it comes to financing retraining.
Is it worth retraining?
Short answer: yes. According to an IAB analysis, retraining improves the long-term prospects of a second career significantly, in certain occupations even enormously. The Institute for Employment Research (IAB) observed the unemployed over a period of four years who had participated in a retraining measure and compared their career to that of comparable unemployed persons who could not be retrained.
Result: Unemployed people who take part in retraining in a recognized training occupation significantly increase their medium to long-term chances of finding employment subject to social security contributions.

The effect is similar in women. Retraining courses in health professions, commercial office professions and transport professions were particularly successful here.
Retraining requirements
First of all, the requirements for retraining depend on the respective occupation and the provider or provider of the retraining measure. In addition to these admission requirements, retraining students are primarily interested in the requirements so that the employment agency supports retraining.
The following applies here: You must be at least 18 years old and have already completed (or at least started) vocational training. Otherwise it is an initial training. However, regardless of the requirements, there is no entitlement to retraining. It is a so-called can-do achievement. The clerk at the employment office or the job center decides on a case-by-case basis whether or not to support and pay for retraining. So there is no guarantee.
These prerequisites make funding more likely:
- Occupational disability
If you can no longer practice the profession you have learned for health reasons, you have a good chance of retraining. As a result of the reorientation, the ability to work can be established in another area. - Bad prospects for the future
These include, above all, occupational profiles and jobs in industries and sectors that are in a state of great upheaval. Outsourcing abroad or discontinuation due to technical developments can be responsible for this. This argument works all the more if the applicant soon becomes unemployed or has been out of work for a long time. - Good perspective
If you want to retrain in a booming industry, you also have good prospects of being approved for retraining. Or choose a profession that suffers from a severe shortage of skilled workers. The better your perspective after retraining, the greater the chance of promotion.
Retraining: which professions are in demand?
Most Germans were retrained for these professions last year. Often because there is currently the greatest demand for these popular retraining occupations and later skilled workers and retraining is promoted accordingly. Of course, this can change from year to year.
- Geriatric nurse
- Office clerk
- Secretary
- Specialist warehouse clerk
- Tax clerk
- Saleswoman
- IT specialist
- Forwarding agent
- Mechatronics technician
- Industrial clerk
Financing retraining
Retraining can be expensive. That is why the financing should be clarified. In general, the following applies: The agency or institution whose services you receive is responsible. The respective clerks are then also your contact persons. Means: The first way for a retraining should always lead to the employment agency or the job center. Here you can find important information, offers and the final answer to the question of who bears the costs for the measure and takes over the financing.
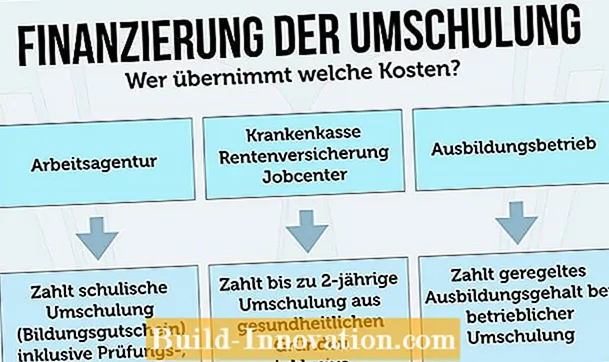
You can also apply for the following funding for retraining:
- Financing of teaching materials
In addition to the actual course costs, additional costs can be covered - for example for required learning materials, work clothes, examination pieces and examination fees. - Financing the travel expenses
You can have the costs for the daily journey between your home and the training center reimbursed. In the event of a temporary change of residence, the employment agency or job center takes on a one-time trip to the training facility and once a month a trip to the previous home town. - Financing of accommodation and meals
Retraining students can also have an external accommodation financed if the training center is too far away. In this case, up to 340 euros for rent and a further 136 euros for meals are granted. - Funding of child care
For children under 15 years of age, the care costs of up to 130 euros per child are covered per month. In this way, retraining participants do not have to waste themselves between attending the measure and looking after the children.
Tips for a successful retraining
If you can convince your clerk, you must apply for funding. Important: Be sure to get the confirmation in writing! The retraining is then financed through an education voucher. However, the amount of funding and funding can vary from case to case.
In order to make the preparation, application and the funding process easier for you, we have put together the most important tips here:
- Active selection
The selection of the right retraining already shows whether employees are committed or not. Institutions such as the employment agency or the pension insurance usually specify which courses should be attended. It is better if you think about it yourself and actively help shape the retraining. - Extensive research
Make a professional and good impression by always being informed. What are the realistic chances after retraining? What is the job market like, what about job offers in your region? You can also find out more in online job exchanges such as Karrieresprung.de. - Own preparation
Of course, all necessary technical content is conveyed in the retraining. Nevertheless, you should begin to read up on the new professional field in advance. This makes it easier to get started on the course and ensures more success. In addition, initiative has never hurt. - Look for practitioners
Many retraining courses are dual. Retraining providers often have practice partners, but you may be able to find them yourself. Those who take care of suitable companies can immediately gain practical experience with potential employers. - Apply early
For many retraining providers, it is common for entire courses and cohorts to start looking for a job more or less at the same time. Of course, this reduces the individual's chances if all participants apply at the same time. It is better to start your job search early and send your first applications before everyone else starts. - Document applications
In your own interest, you should document all of your application activities. It is advisable to keep an application diary in which you record exactly when, how often and where you applied. This is often required as part of retraining. But you will also benefit yourself if you can keep track of things and learn from rejections. - Use practical phases
When it comes to the application, it is essential that you follow up on the practical phases of the retraining. Maybe there is an opportunity to be taken over. Of course, this only works if you are remembered with good performance and an excellent overall impression.



